Understanding GPU Idle Temperature: A Beginner’s Guide
Understanding your GPU’s idle temperature is crucial when it comes to maintaining optimum PC performance and extending the lifespan of your graphics card.
Whether you’re a casual user or a hardcore gamer, knowing what’s considered normal and when there might be cause for concern can save you from potential hardware headaches down the line.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive deep into all aspects of GPU idle temp – discussing normal temperature ranges for various manufacturers, factors that impact temperatures, how to monitor temps effectively, and steps you can take to ensure smooth operation.
What is GPU Idle Temperature?
GPU idle temperature refers to the baseline heat level of a graphics processing unit (GPU) when it is not actively engaged in resource-intensive tasks.
Essentially, this is the temperature your GPU operates at while you’re simply browsing the internet or working on a document, as opposed to running heavy-load apps like modern video games or 3D-rendering software.
For instance, let’s imagine you have an Nvidia RTX 3080 graphics card that typically idles at around 40°C when properly cooled and maintained.
If one day, you find its idle temperature suddenly hovering between 70-85°C – which are more common figures during gaming sessions – without any significant changes in workload, it may signal issues such as dust build-up blocking airflow or old thermal paste losing its effectiveness in conducting heat away from the GPU chip.
Factors That Affect GPU Idle Temperature
Numerous factors contribute to the GPU idle temperature, which can have a significant impact on overall performance and longevity. These factors include:
- Ambient temperature: The temperature of the room where the computer is placed can directly affect the GPU’s temperature.
- PC case ventilation: A well-ventilated case facilitates better airflow, helping to keep the GPU cooler.
- Cooling system quality: The efficiency of your GPU’s cooling system, such as fans or water cooling loops, plays a crucial role in maintaining an optimal idle temperature.
- Dust and debris accumulation: Over time, dust buildup on the GPU and its surrounding components can hinder heat dissipation and raise temperatures.
- Age of the GPU: Older GPUs may be less efficient at managing heat, leading to higher idle temperatures.
- GPU model and manufacturer: Different graphics card models have varying idle temperature ranges based on their design and components.
- Overclocking settings: Pushing a GPU beyond its factory settings may result in higher idle temperatures due to increased power consumption.
- Driver version: Certain drivers may improve or worsen heat management depending on how they interact with the hardware.
- Software running in the background: Some applications or processes running in the background may cause slight increases in GPU utilization rate even when not actively used, raising its idling temperature.
By considering these factors, users can better understand their GPU’s idle temperature behavior and take corrective actions if necessary for improved performance and longevity.
Normal GPU Idle Temperature
The normal idle temperature for Nvidia and AMD GPUs should be around 30 to 40 degrees Celsius, but it’s important to understand how factors such as room temperature and PC ventilation can affect this.
Nvidia GPUs
Nvidia GPUs are known for their exceptional performance in gaming and other graphics-intensive tasks. These powerful cards typically have a normal idle temperature range of 30-40°C, but can reach up to 60-85°C when under high workloads.
Certain factors such as poor cable management, excessive dust buildup, and high ambient temperatures can contribute to overheating issues with Nvidia cards.
One popular card, the Nvidia RTX 3080, has a maximum temperature of 93 degrees Celsius; however, experts recommend keeping temperatures below 80 degrees Celsius for longevity and stability.
AMD GPUs
AMD GPUs, like their Nvidia counterparts, are designed to operate within a specific temperature range. The normal idle temperature for AMD GPUs is between 30-40°C, which can rise by 10-15 degrees Celsius when overclocked.
Running too many tasks simultaneously can cause AMD GPUs to work overtime and lead to higher temperatures.
Additionally, poor airflow/cooling caused by dust or poor ventilation within the PC case can also contribute significantly to overheating of the GPU.
Intel GPUs
Intel GPUs have a normal operating temperature range and temperatures within this range are considered safe. In general, they tend to run cooler than Nvidia or AMD GPUs due to the lower power consumption of integrated graphics.
It’s important to note that some Intel processors have built-in graphics capabilities while others require a separate dedicated graphics card.
Integrated graphics usually have lower performance and consume less power than dedicated ones but may not be powerful enough for certain tasks like gaming or 3D rendering.
GPU Temperature During Load
During gaming, video editing, or 3D rendering, the GPU temperature can climb up to dangerous levels of over 85°C.
Gaming

Playing video games on your computer can put a significant workload on your GPU, causing it to heat up quickly. While gaming, the temperature of your graphics card should remain below 85°C.
If you’re using Nvidia’s or AMD’s high-end GPUs, they shouldn’t exceed 70-85°C during gameplay. It is also crucial to consider the resolution at which you are playing games and how it affects the GPU temperature.
A well-ventilated case that ensures adequate airflow can help lower the GPU’s temperature during gaming sessions by enhancing air circulation inside the case and directing hot air out of it.
You may also want to consider adjusting fan speed or applying fresh thermal paste for efficient cooling elements in addition to cleaning any dirt or debris that could clog up fans and reduce ventilation system performance.
Video Editing
Video editing is a graphics-intensive task that requires a lot of power and can put a strain on your GPU. When video editing, it’s common for the temperature to rise above normal idle temperatures but should not go beyond 80°C.
AMD GPUs such as the RX 6800 XT and Nvidia GPUs like the RTX 3080 are popular choices for video editors due to their high memory capacity and excellent performance under load.
However, running heavy-load apps like Adobe Premiere Pro or Davinci Resolve might cause your GPU temperatures to spike, so ensuring you have adequate cooling is essential.
3D Rendering
3D rendering is a highly-intensive task for graphics cards and can cause temperatures to rise quickly. The high workload requires the GPU to use its processing power consistently, resulting in increased heat output.
To ease the load on your GPU while conducting a 3D rendering job, ensure that you have proper cooling and ventilation systems in place. Also, consider upgrading your graphics card if it’s not powerful enough for such workloads.
Additionally, lowering the quality settings or adjusting fan speeds may be necessary if your GPU temperature rises too high during any heavy-load applications like video editing or gaming.
Causes Of High GPU Idle Temperature
High GPU idle temperature may be caused by poor airflow/cooling, dirt and dust buildup, overclocking, old thermal paste, or malware.
Poor Airflow/cooling
Improper airflow can lead to high GPU idle temperatures and damage your equipment. Your computer components generate heat, and it’s crucial to have proper ventilation in place to allow that heat to escape.
When cables obstruct the internal airflow or there are not enough fans, this prevents hot air from escaping, which causes overheating. High room temperature or the placement of the computer in an area with little air circulation will also exacerbate conditions leading to higher temperatures.
Poor cable management is one primary cause of increased GPU idle temps; when wiring blocks fan movement or restricts airflow, it’ll result in reduced cooling efficiency and lower performance quality overall.
Dirt And Dust
Dirt and dust are common culprits of high GPU idle temperature. When left unchecked, a buildup of dirt and debris on the graphics card can obstruct airflow, causing heat to accumulate in the system.
This leads to increased stress on the components and reduces GPU lifespan. To prevent this, it’s recommended to clean your GPU every six months using compressed air or specialized cleaning tools.
Regularly clearing out your PC case of dust and optimizing cable management can also help improve airflow and reduce temperatures.
Overclocking
Overclocking is the process of increasing the clock speed of a GPU beyond its factory settings to boost performance. While this can improve gaming and other graphics-intensive tasks, it also increases heat production and puts additional strain on your system.
Overclocking can cause GPU temperatures to increase by 10-15 degrees Celsius, which may impede overall performance or even damage your hardware in the long run.
Old Thermal Paste
Old thermal paste can cause high GPU idle temperatures, leading to reduced performance and potentially damaging the hardware.
Over time, thermal paste deteriorates and becomes less effective at transferring heat away from the GPU. This can result in an increase in temperature since the heat generated by the GPU is not being dissipated efficiently.
In addition, reapplying thermal paste can also improve overall performance. When the CPU or GPU heats up beyond its optimal temperature range, it may begin to throttle itself down automatically, reducing clock speeds to maintain safe temperatures.
This can severely impact gaming performance by causing stuttering or decreased frame rates.
Malware
Malware can be a sneaky culprit behind high GPU idle temperatures. It’s essential to keep an eye on the temperature value of your system’s GPU, even when it is not in use, as malware can put it at a load and elevate its temperature.
To prevent this from happening, ensure that you have up-to-date antivirus software installed on your computer. Regularly running virus scans will help detect any malware that may be affecting your system’s performance.
Additionally, it’s crucial to practice safe browsing habits and avoid downloading any suspicious files or visiting unsecured websites that could potentially contain harmful viruses or malware.
How To Measure GPU Temperature
To measure your GPU temperature, you can either use built-in Windows 10 feature or download third-party apps such as MSI Afterburner, CPUID GPU-Z, and Speccy.
Built-in Windows 10/11 Feature
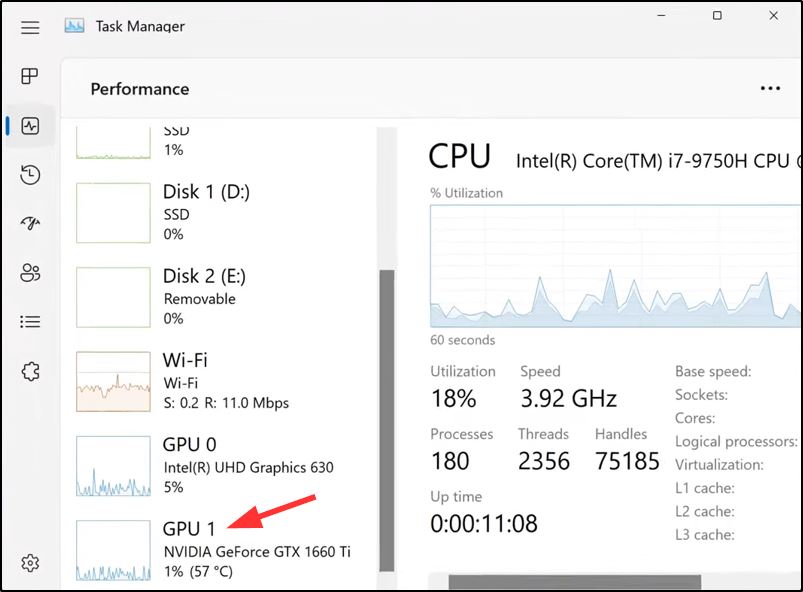
Windows 10 and 11 comes equipped with a built-in feature for measuring GPU temperature, allowing users to easily monitor their graphics card’s performance. To access this feature, simply open up the Task Manager and click on the “Performance” tab.
This is an incredibly useful tool for gamers and other heavy-load applications such as video editing or 3D rendering. Being able to keep track of your GPU’s temperature can help ensure that it doesn’t overheat during intensive tasks, which could ultimately lead to permanent hardware damage if not addressed promptly.
Third-party Apps (e.g., GPU-Z)
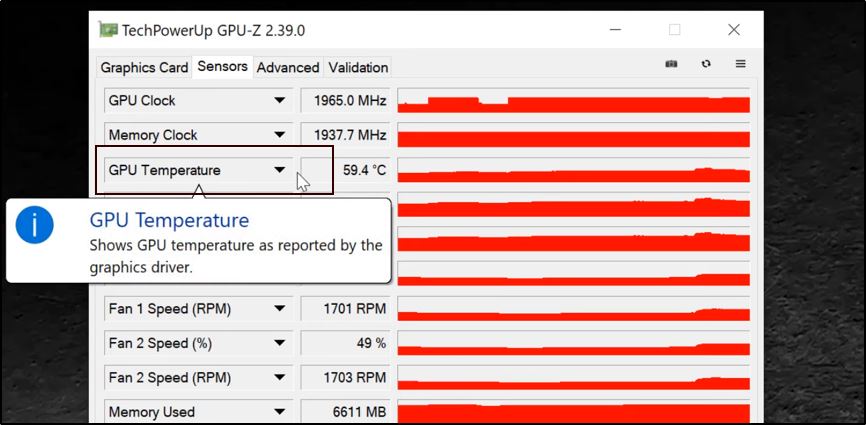
Third-party apps like GPU-Z are essential in checking the temperature of a GPU since Windows 11, 10 and Windows 7 do not come with built-in GPU temperature monitors.
These third-party apps provide real-time information on the temperature of the graphics card, allowing users to monitor its performance closely. Other useful third-party apps for monitoring GPU performance include MSI Afterburner and CPUID HWMonitor.
In addition to helping monitor GPU temperatures, these third-party applications also provide additional features such as overclocking capabilities and fan speed control.
This allows users to adjust settings easily according to their preferences while ensuring that their GPUs run smoothly and efficiently.
How To Lower GPU Idle Temperature
Cleaning the GPU regularly and improving airflow by adjusting fan speed or adding more fans can significantly lower idle temperature.
Cleaning The GPU
Cleaning the GPU is an essential part of maintaining its overall health and longevity. Over time, dust and debris can accumulate in the fan blades and other components, causing restricted airflow that results in increased temperatures.
To prevent this from happening, it’s important to regularly clean your GPU using compressed air or a soft brush. This will remove any dirt or debris clogging up the fan blades and improve airflow throughout your system.
Additionally, proper cable management can help ensure unobstructed ventilation paths for hot air to escape.
Improving Airflow
To help lower GPU idle temperature, improving airflow is critical. Proper ventilation will keep your graphics card from overheating and extend its lifespan. Start by checking that the PC case has enough room for air to move freely through it without any obstructions.
You can improve airflow further by adding more case fans or upgrading them if necessary. You may also consider using liquid cooling systems or external fan setups which are specifically designed to cool high-end GPUs like Nvidia RTX 3080 effectively.
Additionally, regularly cleaning dust and debris off components can prevent clogging and promote efficient heat dissipation while also reducing strain on the GPU’s cooling fans.
Adjusting Fan Speed
Controlling the GPU fan speed is an effective way to lower GPU temperatures. The speed at which fans operate affects how much heat the graphics card generates and how quickly that heat dissipates from the device.
Programs like MSI Afterburner provide an easy-to-use interface for adjusting fan speeds manually or setting up predefined profiles, allowing users to customize their fan settings based on personal preferences or specific usage scenarios.
For instance, when running heavy-load apps such as video editing software or gaming, increasing fan speed can help prevent overheating and improve performance by maintaining a stable temperature level.
Applying Fresh Thermal Paste
Fresh thermal paste is an essential component when it comes to maintaining a healthy GPU temperature. Over time, the thermal paste on your GPU can become dry or cracked, resulting in poor heat transfer and higher temperatures.
Applying fresh thermal paste every year is recommended to prevent bad or no thermal paste from causing GPU temperature issues. This process involves removing the old thermal paste using rubbing alcohol or a specialized cleaner and applying a small amount of new thermal paste onto the GPU before reattaching the cooler.
Fresh thermal paste can help reduce idle and load temperatures by several degrees, which ultimately improves system performance and longevity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the GPU idle temperature is crucial for maximizing your graphics card’s lifespan and performance. While it’s normal for GPUs to reach high temperatures under heavy workload, such as gaming or video editing, keeping it below 85°C is essential to avoid overheating.
Regular maintenance, such as cleaning the GPU and improving airflow, can also help lower the idle temperature. By monitoring your GPU temperature with third-party apps like MSI Afterburner or CPUID GPU-Z, you can ensure that your computer is running smoothly and efficiently.