Does Overclocking Reduce GPU Lifespan? The Truth Revealed
Overclocking is a popular method for boosting the performance of a GPU. However, many users are concerned about the impact of overclocking on the lifespan of their graphics card.
So, does overclocking reduce GPU lifespan? According to experts, the answer is “Yes.”
When you overclock a GPU, you are pushing it to run faster than the manufacturer intended. This creates additional stress on the components and can result in premature failure if done improperly or for extended periods. While some GPUs may be able to handle overclocking without any issues, others may experience a shorter lifespan due to the increased stress on the hardware.
It is important to note that there are ways to reduce the risk of damaging your GPU when overclocking. By taking the right measures and precautions, such as monitoring temperatures and adjusting fan speeds, you can minimize the impact of overclocking on your GPU’s lifespan. However, it is still important to understand the potential risks and weigh them against the benefits of overclocking before making any decisions.
What is Overclocking?
Overclocking is the process of increasing the clock speed of a component beyond its factory-set limits. In the case of a GPU, this means running it at a higher frequency than it was designed to run at. By doing so, the GPU can process data faster and improve performance in tasks such as gaming, video editing, and other graphics-intensive applications.
Overclocking involves increasing the voltage supplied to the GPU, which in turn generates more heat. This can cause stress on the GPU and potentially damage it if not done correctly. As a result, proper precautions must be taken to ensure that the GPU remains within safe thermal ranges and doesn’t sustain any physical damage.
There are various software tools available that allow users to overclock their GPUs. These tools provide users with the ability to adjust clock speeds, voltages, and other settings to achieve the desired level of performance. It’s important to note that not all GPUs are compatible with overclocking, and some may require modifications to the BIOS or other hardware components to achieve optimal results.
Undervolting is another technique used in overclocking that involves reducing the voltage supplied to the GPU to reduce heat generation and improve stability. This can be useful for users who want to overclock their GPUs but are concerned about the potential damage caused by increased heat.
Overall, overclocking can be a useful technique for improving GPU performance, but it must be done with caution and proper precautions to avoid damage to the component. It’s important to research and understand the risks involved before attempting to overclock a GPU.
Does Overclocking Reduce GPU Lifespan?
When it comes to overclocking a GPU, one of the most common concerns is whether it reduces its lifespan. The answer is yes, overclocking can reduce GPU lifespan, but it depends on several factors.
Factors that Affect GPU Lifespan
The lifespan of a GPU depends on various factors, such as voltage, clock speed, heat, and temperature. Overclocking can increase the voltage and clock speed of a GPU, which in turn generates more heat and raises the temperature. This increase in temperature puts extra stress on the components of the GPU, which can lead to damage and premature failure.
Here are the factors that can affect the lifespan of a GPU:
Voltage
Overclocking often involves increasing the voltage supplied to the GPU to sustain higher clock speeds. Higher voltages can result in increased electrical stress on the components, potentially leading to premature failure.
Clock Speed
Overclocking pushes the GPU to run at higher clock speeds than its default settings. While this can improve performance, it also generates more heat and increases the workload on the GPU’s components, which can contribute to their degradation over time.
Heat
Overclocking produces more heat due to increased voltage and clock speeds. Elevated temperatures can accelerate the wear and tear of the GPU’s components, potentially leading to malfunctions or failure.
Temperature
When a GPU is overclocked, it tends to operate at higher temperatures than under normal conditions. Prolonged exposure to high temperatures can weaken solder joints, degrade capacitors, and cause other components to fail, reducing the GPU’s lifespan.
Cooling
Overclocking often necessitates enhanced cooling measures to dissipate the extra heat generated. Insufficient cooling can result in even higher temperatures, increasing the risk of component damage and reducing the GPU’s longevity.
Silicon Lottery
Each GPU is unique, and some chips overclock better than others. This phenomenon is often referred to as the “silicon lottery.” GPUs that overclock poorly may experience more significant degradation over time compared to those that overclock well.
Quality of Components
The quality of the GPU’s components can also influence its lifespan. Higher-quality components are generally more durable and better equipped to handle the stresses associated with overclocking. GPUs with superior cooling systems and build quality tend to have a better chance of withstanding the effects of overclocking.
It’s important to note that these factors interact with one another and can vary depending on the specific GPU model and manufacturer. Therefore, it is crucial to consider these factors and exercise caution when overclocking to minimize the potential impact on the GPU’s lifespan.
How Overclocking Affects GPU Lifespan

Overclocking can have an impact on the lifespan of a GPU due to the increased stress placed on its components. When you overclock a GPU, you are essentially pushing it beyond its factory-set specifications, running it at higher voltages and clock speeds to achieve better performance. While this can result in increased power and improved graphical capabilities, it also generates more heat and puts additional strain on the GPU’s hardware.
Heat is one of the primary factors that can degrade the components of a GPU over time. As the GPU operates at higher clock speeds and voltages, it generates more heat than under normal operating conditions. The increased heat can cause the GPU to reach higher temperatures, which can have detrimental effects on its longevity.
Prolonged exposure to high temperatures can lead to the weakening of solder joints, degradation of capacitors, and other forms of component damage. Over time, this can result in malfunctions, instability, or even complete failure of the GPU.
Furthermore, higher voltages and clock speeds also increase the electrical stress on the GPU’s components. The increased electrical stress can lead to electro migration, which is the movement of metal atoms within the GPU’s transistors. Over time, electromigration can cause transistor degradation and impact the overall functionality and reliability of the GPU.
It’s important to note that the degree to which overclocking affects the GPU lifespan depends on several factors. These include the extent of the overclock (how much higher you push the voltage and clock speeds), the cooling solution employed to dissipate the increased heat, and the overall quality and design of the GPU.
Overall, while overclocking can provide a performance boost, it also carries the risk of reducing the GPU’s lifespan. The extent to which overclocking affects the GPU’s lifespan depends on various factors, including the degree of overclock, cooling solutions, and overall GPU quality. It’s important to weigh the potential benefits against the risks and make informed decisions when considering overclocking your GPU.
How to Minimize the Impact of Overclocking on GPU Lifespan?
To maximize the lifespan of your overclocked GPU, it’s essential to follow safe overclocking practices. Here are some tips to keep in mind:
- Incremental Overclocking: Instead of making significant jumps in clock speeds, incrementally increase them in small increments. This allows you to find the GPU’s stable limits while minimizing the risk of damaging it.
- Stress Testing: After each overclocking adjustment, stress test your GPU using reliable benchmarking tools. Stress testing helps identify stability issues and ensures that your overclocked settings are sustainable.
- Monitor Temperatures: Keep a close eye on your GPU temperatures during overclocking. Excessive temperatures can lead to thermal throttling and potential damage. Aim to keep temperatures within safe ranges.
- Maintain Adequate Power Supply: Overclocking increases power consumption. Ensure that your power supply unit (PSU) can handle the additional load to prevent stability issues and potential damage to your GPU.
Can I Leave My GPU Overclocked All the Time?
While it is technically possible to leave your GPU overclocked all the time, it is generally not recommended.
Overclocking increases the clock frequencies and voltage of your GPU, which can lead to higher power consumption, increased heat generation, and potentially reduced lifespan of the GPU.
Leaving your GPU overclocked constantly can result in higher operating temperatures, which may exceed the manufacturer’s recommended limits. This can lead to instability, crashes, or even permanent damage to the GPU.
It is advisable to use overclocking for specific tasks or gaming sessions when you require extra performance, and revert to default settings for everyday use. Many overclocking utilities, including MSI Afterburner, allow you to save profiles, making it convenient to switch between overclocked and default settings.
Regularly monitoring your GPU’s temperature and ensuring it remains within safe operating limits is crucial. If you notice any signs of instability or excessive heat, it is recommended to revert to default settings or reduce the overclock for the long-term health and reliability of your GPU.
What is the Average Lifespan of an Overclocked GPU
Determining the exact lifespan of an overclocked GPU in terms of years is challenging due to various factors involved. The lifespan of a GPU can vary greatly depending on usage, environmental conditions, maintenance, and individual component quality. However, it is possible to provide a general estimate based on typical scenarios:
- Moderate Overclocking: If a GPU is overclocked conservatively within safe limits, with proper cooling and voltage management, it can generally last as long as a non-overclocked GPU. In this case, you can expect a typical lifespan of around 3 to 5 years, which is the average lifespan of many high-quality GPUs.
- Aggressive Overclocking: If a GPU is heavily overclocked, pushing it to its limits and operating at higher temperatures for extended periods, its lifespan may be slightly reduced. In such cases, the GPU might last around 2 to 4 years. However, it’s important to note that this is a rough estimate, and individual results can vary.
It’s worth mentioning that these estimations assume reasonable usage patterns, adequate cooling, and appropriate voltage management. Additionally, the quality of the GPU, manufacturing processes, and other external factors can also influence lifespan.
How to Overclock a GPU Safely
Before starting the process of overclocking a GPU, it is important to have the right tools. The following tools are necessary to overclock a GPU safely:
- MSI Afterburner or similar software to modify GPU settings
- Good thermal paste to ensure efficient heat transfer
- CPU cooler or cooling system to keep the CPU and GPU cool
- Undervolting to reduce the voltage and power consumption of the GPU
- V-sync to avoid screen tearing
- CPU cores to balance the load between the CPU and GPU
- Hertz or gigahertz to set the clock rate of the GPU
- Transistors to control the flow of electricity in the GPU
- Silicon lottery to determine the quality of the GPU
- Frames per second to measure the performance of the GPU
- Applications to test the stability and performance of the GPU
- Cleaning tools to remove debris from the cooling system
- Ventilation and coolers to ensure proper airflow
- XMP to set the memory speed of the GPU
- PSU or power supply to provide enough power for the GPU
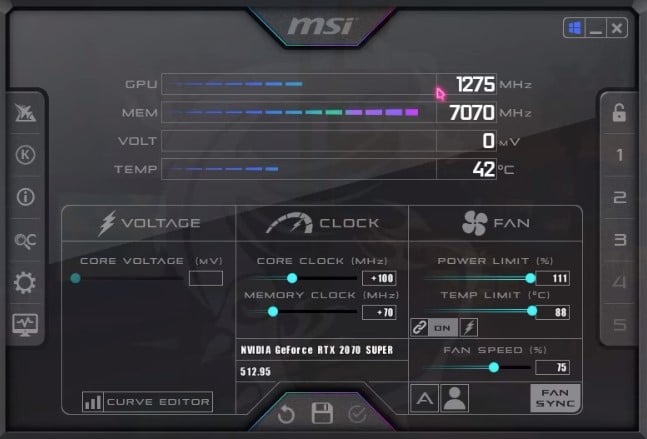
Steps to Safely Overclock a GPU
Overclocking a GPU can be risky, but following these steps can help minimize the risk:
Step 1: Download and install MSI Afterburner from the official website.
Step 2: Launch MSI Afterburner and make sure your GPU is detected.
Step 3: In the settings menu, select the “Monitoring” tab. Check the box next to “GPU Temperature” and click “OK” to save the settings.
Step 4: Increase the “Core Clock” slider by a small increment, such as 10 MHz, and click the “Apply” button.
Step 5: If the GPU is stable and performs well, save the settings and use them for gaming or other tasks.
Remember to monitor your GPU’s temperature and be cautious when overclocking.
How to Monitor GPU Temperature and Performance
Monitoring the GPU temperature and performance is crucial when overclocking a GPU. MSI Afterburner or similar software can be used to monitor the GPU temperature and performance.
The following steps can help monitor the GPU temperature and performance:
- Open MSI Afterburner or similar software.
- Check the GPU temperature and performance in the main window.
- Use the graphs and charts to monitor the GPU temperature and performance over time.
- Adjust the cooling system if the GPU temperature is too high.
How to Test Stability and Performance
Testing the stability and performance of the GPU is important to ensure that the GPU is working properly and safely.
The following steps can help test the stability and performance of the GPU:
- Use applications like FurMark or 3DMark to stress test the GPU.
- Monitor the GPU temperature and performance during the stress test.
- Check for artifacts, crashes, or other issues during the stress test.
- Adjust the clock rate and voltage if the GPU is unstable or performs poorly.
By following these steps, users can safely overclock their GPU and enjoy improved performance while minimizing the risk of damage or instability.
Signs of GPU Degradation
Over time, an overclocked GPU may exhibit signs of degradation. These signs can include:
- Artifacts: Visual artifacts such as flickering, screen tearing, or unusual graphical glitches during gameplay may indicate GPU instability.
- Driver Crashes: Frequent driver crashes or system instability during resource-intensive tasks could be indicative of an overclocked GPU struggling to maintain stability.
- Performance Deterioration: If you notice a significant drop in performance compared to when the GPU was first overclocked, it may be a sign of degradation.
- Increased Fan Noise: As the GPU ages and components wear out, you may notice increased fan noise due to the need for higher fan speeds to maintain adequate cooling.
How to Prolong Your Overclocked GPU’s Lifespan
While the lifespan of an overclocked GPU can be influenced by various factors, there are steps you can take to maximize its longevity. Here are some recommendations:
Ensure Proper Cooling
As mentioned earlier, maintaining proper cooling is crucial for an overclocked GPU. Regularly clean dust from your PC case and ensure good airflow to prevent excessive heat buildup.
Avoid Excessive Voltage
While increasing voltage can improve stability during overclocking, excessive voltage can lead to premature degradation. Find a balance between performance and voltage to avoid unnecessary strain on the GPU.
Regularly Maintain Your GPU

Cleaning the GPU’s fans and heatsinks periodically helps remove dust and maintain optimal cooling efficiency. Be sure to follow manufacturer guidelines when cleaning or applying thermal paste.
Avoid Extreme Ambient Temperatures
Operating your PC in extremely hot or cold environments can negatively impact the GPU’s lifespan. Aim for a moderate ambient temperature range for optimal performance and longevity.
Consider Underclocking for Longevity
If you prioritize GPU longevity over maximum performance, you may opt to underclock your GPU slightly. Underclocking reduces heat generation and can extend the GPU’s lifespan.
Conclusion
In conclusion, overclocking a GPU can have both positive and negative effects on its lifespan. While it can increase performance and improve the overall gaming experience, it can also cause additional stress on the components and reduce the longevity of the hardware.
It is important to note that the impact of overclocking on the GPU lifespan can vary depending on several factors, including the quality of the cooling system, the hardware components used, and the compatibility with the motherboard.
To avoid reducing the lifespan of the GPU, it is recommended to monitor the temperatures, clean the GPU regularly, and avoid overclocking it all the time. Additionally, enabling V-sync and reducing the voltages can also help to prolong the GPU’s lifespan.
Overall, while overclocking can provide a boost in performance, it is important to weigh the potential benefits against the risks and take the necessary precautions to ensure the longevity of the hardware.